Plastic is a versatile material used in countless applications, from DIY projects and crafts to professional signage and prototypes. Cutting plastic correctly is essential to achieve clean edges, accurate shapes, and professional results. The ideal method depends on the type of plastic, its thickness, and the level of precision required.
In this guide, we'll explore 4 effective ways to cut plastic, from high-tech laser cutting to simple utility knife scoring—so you can choose the method that best fits your project and tools.

In this article:
- Method 1: Cut Plastic with a Laser Cutter
- Method 2: Cut Plastic with a Utility Knife
- Method 3: Cut Plastic with a Saw
- Method 4: Cut Plastic via String Slicing
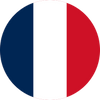
Method 1: Cut Plastic with a Laser Cutter
A laser cutter uses a focused beam of light to cut through plastic with high precision.
It's ideal for creating clean, intricate shapes and designs without the need for additional finishing. Laser cutting works well for many thermoplastics, but some materials, like PVC, should never be used due to toxic fumes.
Best for:
- Thin to medium plastic sheets
- Intricate designs, patterns, and custom shapes
- Projects requiring smooth, polished edges straight from the machine
Precision Level of Cutting Plastic with a Laser Cutter
Very High — Can achieve fine details and consistent, repeatable cuts
Edge Finish Quality of Cutting Plastic with a Laser Cutter
High — Produces smooth, clean edges; usually requires little to no post-processing.
Best Thickness Range
Typically 1 mm – 12 mm (1/32″ – 1/2″) depending on laser power and type of plastic. Thicker plastics may require multiple passes or higher-powered machines.
Pros and Cons of Cutting Plastic with a Laser Cutter
Pros
- Extremely precise and repeatable
- Clean, polished edges with minimal finishing
- Can cut complex shapes and designs easily
Cons
- Not suitable for plastics that release toxic gases (e.g., PVC)
- Produces fumes — requires proper ventilation
Method 2: Cut Plastic with a Utility Knife
Cutting plastic with a utility knife is a simple, low-cost method best suited for thin sheet materials. The process typically involves scoring along a straight line multiple times and then snapping the plastic along the scored groove.
This approach requires minimal equipment, produces no power tool noise, and is ideal for small, precise jobs on softer plastics.
Best for:
- Thin sheet plastics like acrylic, polystyrene, PVC, or PETG
- Straight cuts on small projects
- Quick adjustments or on-site trimming
Precision Level of Cutting Plastic with a Utility Knife
Medium — Accurate for straight lines when used with a ruler or guide; not suitable for curves or intricate shapes.
Edge Finish Quality of Cutting Plastic with a Utility Knife
Medium–Low — Snapped edges are functional but may require sanding for a clean, smooth finish.
Best Thickness Range
Up to 3 mm (1/8″) for most plastics. Some softer plastics can be cut up to ~5 mm with patience and repeated scoring
Pros and Cons of Cutting Plastic with a Utility Knife
Pros
- Portable and easy to use
- Quiet and dust-free
Cons
- Limited to thin plastics
- Only practical for straight cuts
- Requires multiple passes and effort on harder materials
Method 3: Cut Plastic with a Saw
Cutting plastic with saws is a versatile and reliable method suitable for a wide range of plastic types and thicknesses.
Common tools include hand saws, circular saws, jigsaws, and table saws equipped with fine-tooth blades designed for plastic or soft materials. This method is ideal for straight cuts, larger pieces, and projects requiring moderate precision.
Best for:
- Medium to thick plastic sheets or blocks
- Straight or slightly curved cuts
Precision Level of Cutting Plastic with a Saw
Medium–High — Accurate with proper guides, fences, or jigs; less suitable for intricate, detailed shapes.
Edge Finish Quality of Cutting Plastic with a Saw
Medium — Edges may show saw marks and require sanding or polishing; risk of chipping if the wrong blade or feed rate is used.
Best Thickness Range
Works well for thin to thick plastics: 2 mm – 25 mm (1/16″ – 1″). Very thin sheets may crack if not properly supported
Pros and Cons of Cutting Plastic with a Saw
Pros
- Handles larger and thicker pieces efficiently
- Can make straight or basic curved cuts
- Suitable for a wide variety of plastic types
Cons
- Edges usually need post-processing
- Not ideal for intricate or highly detailed shapes
- Produces dust and noise
Method 4: Cut Plastic via String Slicing
String slicing is a heat-based method for cutting soft plastics. A taut string or wire is heated, then used to melt through the plastic along the desired line. This technique is simple and doesn't require complex tools, but it's mainly suitable for thin, soft plastics rather than rigid materials.
Best for:
- Soft thermoplastics such as thin PVC, polyethylene, or polypropylene
- Small-scale cuts where precision is less critical
Precision Level of Cutting Plastic via String Slicing
Low–Medium — Works for simple straight cuts, but fine details or curves are difficult to control accurately.
Edge Finish Quality of Cutting Plastic via String Slicing
Low–Medium — Edges may be rough, slightly melted, or uneven; usually requires sanding or filing afterward.
Best Thickness Range
Up to 5 mm (1/4″) for most soft plastics. Not suitable for hard or thick sheets
Pros and Cons of Cutting Plastic via String Slicing
Pros
- Inexpensive and simple setup
- No power tools needed
- Quick for small or thin pieces
Cons
- Limited to soft, thin plastics
- Edges often need finishing
- Produces fumes — requires ventilation
Conclusion:
Each method for cutting plastic offers unique advantages and limitations. Laser cutting provides precision and smooth, polished edges, while utility knives and scoring are quick, low-cost options for thin sheets. Saws handle larger or thicker pieces efficiently, and string slicing offers a simple, heat-based solution for soft plastics. By understanding these techniques and their best applications, you can select the right approach to achieve clean, accurate cuts and bring your plastic projects to life.